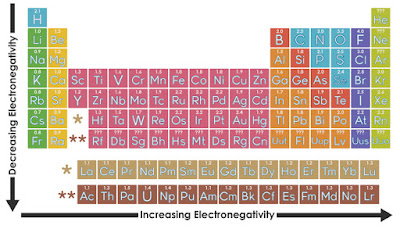
Electronegativity is a
measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. The
higher the electronegativity of an atom, the greater its attraction
for bonding electrons. In an element group, the
electronegativity decreases as atomic number increases, as a result of
increased distance between the valence electron and nucleus (greater
atomic radius). An example of an electropositive (i.e., low
electronegativity) element is cesium; an example of a
highly electronegative element is fluorine.
- Moving left to
right across the periodic table, electronegativity increases.
- Moving top to bottom down
the periodic table, electronegativity decreases.