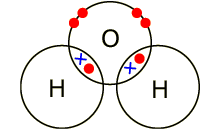
A covalent compound is a
molecule formed by covalent bonds, in which the atoms share one or more pairs
of valence electrons. A covalent bond is a chemical link between two atoms in
which electrons are shared between them.
Example: covalent bond between the
oxygen and hydrogen in a water molecule (H2O). Each of the covalent
bonds contains two electrons - one from a hydrogen atom and one from the oxygen
atom. Both atoms share the electrons.
- Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
- Covalent compounds are mostly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
- Covalent compounds cannot conduct electricity in solid and molten state.