How are the trends of atomic radius and ionization energy related? Explain in both groups and periods.
These trends are inverses of each other. As the size of the atom increases, the ionization energy (energy required to remove the electron) decreases because the electron being removed is farther from the nucleus in a larger atom.Less energy is required to remove an electron further from the nucleus. [AR increases down a group while IE decreases; AR decreases across a period while IE increases.]
What’s the difference between electronegativity and ionization energy?
Electronegativity is related to the pull of a nucleus on an electron being shared in a bond. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an unbonded atom. Electronegativity is a ranking and has no units. Ionization energy is an amount of energy and has units such as kilojoules.
Atomic Radius Trends
Why are atoms larger going down a group
Atoms get larger because the higher the energy level, the more orbitals it has and the further away from the nucleus those orbitals are. Also, more electrons are interfering with the attraction that the nucleus has on the highest energy electrons [shielding].
Why do atoms get smaller going from left to right across the table.
Atoms get smaller because there is an increase in the effective nuclear charge [more protons attracting more electrons) so the highest energy level get pulled in closer to the nucleus.
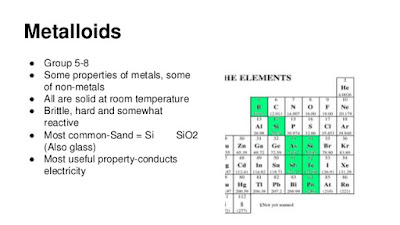
What are metalloids? State the properties of metalloids and list all the metalloids on the Periodic Table.
Metalloids are elements that lie along the zigzag line on the periodic table starting with Boron and moving down in steps. These elements share properties of both metals and non-metals. Metalloids are solids, ductile and malleable. These are good semiconductors. At high temperatures metalloids acts like metals and conduct electricity. At lower temperatures metalloids act like nonmetals and stop electricity from flowing. This property is useful in electronic devices such as computers, tv's and solar cells. The metalloids include: Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic, Antimony, Tellurium, and Polonium.
State three differences between an ionic compound and a covalent compound
- An ionic compound has high boiling and melting point whereas covalent compound has low melting and boiling point.
- An ionic compound is soluble in water but is insoluble in organic solvents, whereas a covalent compounds is soluble in organic solvent but is insouble in water.
- An ionic compounds conducts electricity in the liquid state and in aqueous solution whereas a covalent compounds does not conduct electricity in any state.