SPM Form 4: Periodic Table of elements (Checklist)
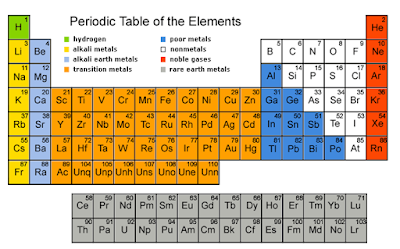
- Periodic Table: the table
showing the elements in order of increasing proton number; similar elements are
arranged in columns called groups.
- Group: A vertical column of
elements in the Periodic table.
- Period: A horizontal row of the
Periodic Table; its number tells you how many electron shells there are.
- Alkali metals: the Group I
elements of the Periodic Table, which include lithium, sodium, potassium,
rubidium, caesium and francium.
- Alkaline earth metals: the
Group II elements of the Periodic Table, which include beryllium, magnesium,
calcium, strontium, barium, and radium.
- Halogens: the Group VII
elements of the Periodic Table, which include fluorine, chlorine, bromine,
iodine and astatine.
- Noble gases: the Group 18
elements of the Periodic Table; they are called ‘noble’ or inert gases because
they are so unreactive, which include helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon and
radon.
- Transition elements: the
elements in the wide middle block of the Periodic Table (elements in group 3 to
group 12).
- Metal: an element that shows
metallic properties (for example conducts electricity, and forms positive ions)
- Non-metal - an element that
does not show metallic properties: the non-metals lie to the right of the zig-zag
line in the Periodic Table.
- Amphoteric oxide: An oxide
that exhibits both acidic and basic properties.
- The atomic radius is a term
used to describe the size of the atom.
- The ionization energy is the
energy required to completely remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion.
- Electron affinity reflects
the ability of an atom to accept an electron. It is the energy change that
occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom.
- Electronegativity is a
measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. The
higher the electronegativity of an atom, the greater its attraction for bonding
electrons.
