SPM Form 4: Manufactured Substances in Industry (Checklist)
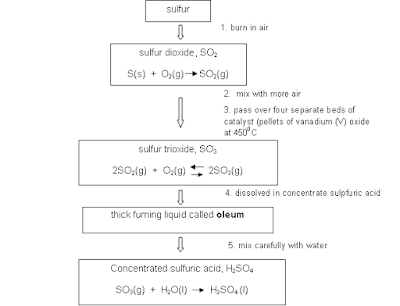
- Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
is a highly corrosive acid made from sulfur dioxide; widely used in the
chemical industry.
- Contact process: the
industrial process for making sulfuric acid.
- Ammonia (NH3) is colorless,
pungent gas composed of nitrogen and hydrogen.

- Haber process: the process
for making ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, in industry.
- Ammonium fertilizer: A salt
that is prepared from the reaction between ammonia and an acid. Ammonium
sulphate, (NH4)2 SO4 which is an ammonium
fertilizer can be prepared from the reaction between ammonia, NH3
solution and sulphuric acid, H2SO4.
- Alloys: A mixture of two or
more elements with certain fixed composition in which the major component is a
metal. Alloy is harder than pure metal.
- Metal corrosion: The gradual
destruction of a metal by reaction with its environmental. Iron rusts faster
than steel. Stainless steel does not rust.
- Polymer: a compound
containing very large molecules, formed by polymerization.
- Synthetic polymers are
derived from petroleum oil, and made by scientists and engineers. Examples of
synthetic polymers include nylon, polyethylene, polyester, Teflon, and epoxy.
- Natural polymers occur in
nature and can be extracted and often water-based. Examples of naturally
occurring polymers are silk, wool, DNA, cellulose and proteins.
- Glass: A homogeneous material
with a random, liquid-like molecular structure.
- Ceramic is a hard, unreactive material
that can withstand high temperatures, made by baking clay in a kiln; ceramics
are non-conductors.
- A "composite"
material is when two or more different materials are combined together to
create a superior and unique material.