SPM Form 4: Acids and Bases (Checklist)
- Acid: A chemical substance
which ionizes in water to produce hydrogen ions. An acid will only show its
acidic properties when it is dissolved in water. E.g. ethanoic acid CH3COOH
only exhibit acidic properties when water is present.
- Alkali: A chemical substance
which ionizes in water to produce hydroxide ions. An alkali will only show its
alkaline properties when it is dissolved in water. E.g. barium hydroxide,
Ba(OH)3 only exhibit alkaline properties when water is present.
- A strong acid is an acid
that is completely dissociated in an aqueous solution. E.g. HCl (hydrochloric
acid), H2SO4 (sulfuric acid), HNO3 (nitric
acid).
- A weak acid is an acid that
is partially dissociated in an aqueous solution. E.g. CH3COOH
- A strong base is a base that
is completely dissociated in an aqueous solution. E.g. KOH, NaOH
- A weak base is a base that
is partially dissociated in an aqueous solution. E.g. NH4OH
- Molarity: The number of
moles of solute in 1 dm3 solution. When the molarity of an acid
increases, its pH value decreases. When the molarity of an alkali increases,
its pH value increases.
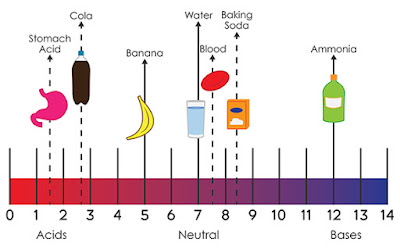
- pH is a measure of hydrogen
ion concentration; a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
Aqueous solutions at 25°C with a pH less than seven are acidic, while those
with a pH greater than seven are basic or alkaline. A pH level of is 7.0 at
25°C is defined as 'neutral' because the concentration of H3O+
equals the concentration of OH− in pure water.
- The two factors which
determine the pH value of an acid or an alkali are degree of ionization and
concentration of the acid or alkali.
- Neutralization: A reaction
between an acid and an alkali or a base to produce salt and water.
- Acid-base titration: A
quantitative analysis to determine the volume of an acid required to exactly
neutralize a fixed volume of an alkali with the help of a suitable indicator.
- End-point: A stage achieved
in titration where the volume of acid added exactly neutralizes a fixed volume
of an alkali.
