- They have usually low melting and boiling points.
- They are usually bad conductors of electricity.
- They are usually insoluble in water but are soluble in non-aqueous solvents like benzene, ether, alcohol and acetone.
- Larger molecules with 3-dimensional bonding form covalent crystals which are very stable and hard. They have very high melting and boiling points.
State the characteristic properties of covalent compounds
Explain why is the BF3 electron deficient.
Boron atom has 3 electrons in its outer most shell. It forms 3 single covalent bonds with fluorine and attains 6 electrons. Boron needs still 2 more electrons to complete its octet. It accepts a lone pair through coordinate covalent bond from another molecule to complete its octet.
State the difference between polar and non-polar covalent bonds.
Non-polar covalent bonds are covalent bond that formed between 2 similar atoms [homo-atoms]; the shared pair of electrons is attracted by both the atoms equally. For example, bond formation in H2 and Cl2. Polar covalent bonds are covalent bonds that formed between 2 different types of atoms [hetro-atoms]; the bond pair of electron will not be attracted equally by the bonded atoms. For example: H2O, HF and HCl.
Formation of hydrogen molecules
Hydrogen atom has one
valency. To become stable with hydrogen atom, it needs one more electron, When
2 hydrogen atoms join, they share their electrons, on which, the share becomes
2 electrons, which is now a noble gas configuration, being shared between these
2 atoms.
H – H single bond [they
share an electron pair (2 electrons)].
State the general properties of ionic compounds and covalent compounds.
General properties of ionic
compounds:
- Solid at room conditions.
- High melting point and boiling point.
- Soluble in water but insoluble in non-polar solvents.
- Do not conduct electricity in the solid state.
- Conduct electricity in molten state or in aqueous solutions.
General properties of
covalent compounds:
- Low boiling point and melting point.
- Insoluble in water but soluble in non-polar solvents.
- Do not conduct electricity, either in the solid or molten state.
Ionic bonds versus Covalent bonds
- In ionic bonds, electron pairs are shared between atoms. In covalent bonds, atoms are electrostatically attracted towards each other.
- Ionic bonds occur through the interaction between cations and anions. Covalent bonds occur through the interaction of neutral atoms.
- Ionic bonds are the strongest type of chemical bond. Covalent bonds are quite weak.
- Metallic elements tend to form ionic bonds. Non-metallic elements tend to form covalent bonds.
Properties of covalent compounds
- It is a hard solid because it consists of many strong covalent bonds between atoms. This property makes it suitable as abrasives.
- It has very high melting and boiling points.
- It does not conduct electricity (except graphite) because there are no free electrons in covalent bonds since they are used to form bonds; hence electrons are in fixed positions. To conduct electricity, there must be free electrons.
- All covalent structures are insoluble in water.
Formation of Oxygen gas
An O atom has 6 valency and
needs 2 electrons, each, to form a noble gas configuration. Hence, each share
the amount of electrons each short of, in this case – 2 electrons, to form
stable molecule. The contribution hence now becomes 4 electrons and what left
on each oxygen atom are 4 electrons. We combine each 4 electrons on oxygen atom
with the 4 electrons shared and hence we get 8 valency for each oxygen atom – a
noble gas configuration!
Formation of Chlorine gas
Cl atom has 7 valency and
needs one electron, each, to form a noble gas configuration between two Cl
atoms. Hence they share an electron each to hence share 2 electrons between the
atoms. Hence, each Cl atom now has 8 valency which is a noble gas
configuration.
Covalent compounds
A covalent compound is a
molecule formed by covalent bonds, in which the atoms share one or more pairs
of valence electrons. A covalent bond is a chemical link between two atoms in
which electrons are shared between them.
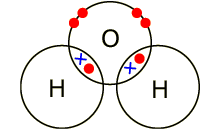
Example: covalent bond between the
oxygen and hydrogen in a water molecule (H2O). Each of the covalent
bonds contains two electrons - one from a hydrogen atom and one from the oxygen
atom. Both atoms share the electrons.
- Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
- Covalent compounds are mostly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
- Covalent compounds cannot conduct electricity in solid and molten state.
SPM Form 4: Chemical Bonds (Checklist)
- An ionic bond is a chemical link between two atoms caused by the electrostatic force between oppositely-charged ions in an ionic compound. Examples: an ionic bond between the sodium and chloride ions in table salt, NaCl.
- A covalent bond is a chemical link between two atoms in which electrons are shared between them. Examples: a covalent bond between the oxygen and hydrogen in a water molecule (H2O).
- Ionic compounds: a compound that consists of positive ions and negative ions arranged in the crystal lattice and are attracted to each other by strong electrostatic forces. Ionic compounds such as magnesium oxide, MgO, sodium chloride, NaCl and iron(III) chloride, FeCl3 can be respectively prepared through a reaction between a metal and a non-metal.
- Covalent compounds are those in which the elements share electrons via covalent bonds.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling point whereas covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
- Ionic compounds are mostly soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. Covalent compounds are mostly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
- Ionic compounds can conduct electricity in molten state but cannot conduct electricity in solid state. Covalent compounds cannot conduct electricity in solid and molten states.
- Melting points: the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid at a fixed pressure.
- Boiling point: the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the external pressure surrounding the liquid.
- Solubility: the maximum quantity of a substance that may be dissolved in another or the maximum amount of solute that may be dissolved in a solvent.