- Simple protein refers to protein that consists of only amino acids and does not contain any other substances. Example: collagen.
- Conjugated protein is a protein that contains non-protein materials called prosthetic groups. Example: haemoglobin.
- The globular protein is a polypeptide chain with tertiary or quaternary structures. It is tightly coiled and folded into a spherical shape. Examples: enzymes, antibodies and some hormones.
Define simple protein, conjugated protein and the globular protein
Amino acids are amphoteric molecules. Explain this statement.
- Amphoteric molecules can act both as a base and an acid.
- Amino acids have both acidic (carboxyl) and basic amino groups.
- At high concentrations of hydrogen ions, the negatively charged carboxyl group will accept protons and become uncharged and the overall charge of the amino acids becomes positive.
- At low concentration of hydrogen ions, the positively charged amino group loses its proton and the overall charge of molecule becomes negative.
State factors that can cause the denaturation of proteins
- Heat or radiation
- Strong acids and alkalis
- High salt concentration and heavy metals
- Detergent and organic solvents
- Mechanical force
Define hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions. State the movement of water in these solutions.
- A hypertonic solution is a solution that has more solutes and it had higher osmotic pressure than other solutions.
- A hypotonic solution is a solution that has fewer solutes and it had lower osmotic pressure than other solutions.
- An isotonic solution refers to a solution that has the same amount of solutes and therefore, the same osmotic pressure with another solution.
- Water tends to diffuse from hypotonic solution to hypertonic solutions and shows no net osmotic pressure movement from one isotonic to another isotonic solution.
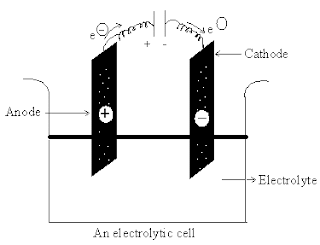
What is electrolysis?
Electrolysis is the
production of a chemical reaction by passing an electric current through an
electrolyte. In electrolysis, positive ions transfer to the cathode and
negative ions to the anode. The reactions occurring depend on electron transfer
at the electrodes and are therefore redox reactions. At the anode, negative
ions in solution may lose electrons to form neutral species. Alternatively,
atoms of the electrode can lose electrons and go into solution as positive
ions. In either case the reaction is an oxidation. At the cathode, positive
ions in solution can gain electrons to form neutral species. Thus cathode
reactions are reductions.
What is electrolyte?
Electrolyte is a liquid that
conducts electricity as a result of the presence of positive or negative ions.
Electrolytes are molten ionic compounds or solutions containing ions, i.e.
solutions of ionic salts or of compounds that ionize in solution. Liquid
metals, in which the conduction is by free electrons, are not usually regarded
as electrolytes. Solid conductors of ions, as in the sodium–sulphur cell, are
also known as electrolytes.
e.g. acids, alkali, salts dissolved in water, molten salts
Explain why water has a high specific heat capacity and it advantages
Water has a high specific
heat capacity because a large amount of thermal energy needs to be absorbed in
order to break the hydrogen bonds among water molecules before the individual
water molecules can begin to move about more freely and therefore, causing an
increase in temperature. A high specific heat capacity allows water to
stabilize the internal temperature of organisms and environments such as large
bodies of water like oceans and ponds.
Define electrophile and nucleophile
Electrophile is an ion or
molecule that is electron deficient and can accept electrons. Electrophiles are
often reducing agents and Lewis acids. They are either positive ions (e.g. NO2+)
or molecules that have a positive charge on a particular atom (e.g. SO3,
which has an electron deficient sulphur atom). In organic reactions they tend
to attack negatively charged parts of a molecule. Types of electrophiles: Lewis
acids, cations and electron deficient sites in organic compounds
Nucleophile is an ion or
molecule that can donate electrons. Nucleophiles are often oxidizing agents and
Lewis bases. They are either negative ions (e.g. Cl–) or molecules
that have electron pairs (e.g. NH3). In organic reactions they tend
to attack positively charged parts of a molecule. Types of nucleophiles: Lewis
bases, anions and electron rich sites in organic compounds.
What is activation energy?
- Activation energy, Ea is the minimum energy required for substances to react. It represents the energy barrier that has to be overcome before a reaction can take place to form products.
- In a reaction, the reactant molecules come together and chemical bonds are stretched, broken, and formed in producing the products.
- During this process the energy of the system increases to a maximum, then decreases to the energy of the products.
- The activation energy is the difference between the maximum energy and the energy of the reactants; i.e. it is the energy barrier that has to be overcome for the reaction to proceed.
- The activation energy determines the way in which the rate of the reaction varies with. It is usual to express activation energies in joules per mole of reactants.